Expert Guide for Electricians and Homeowners
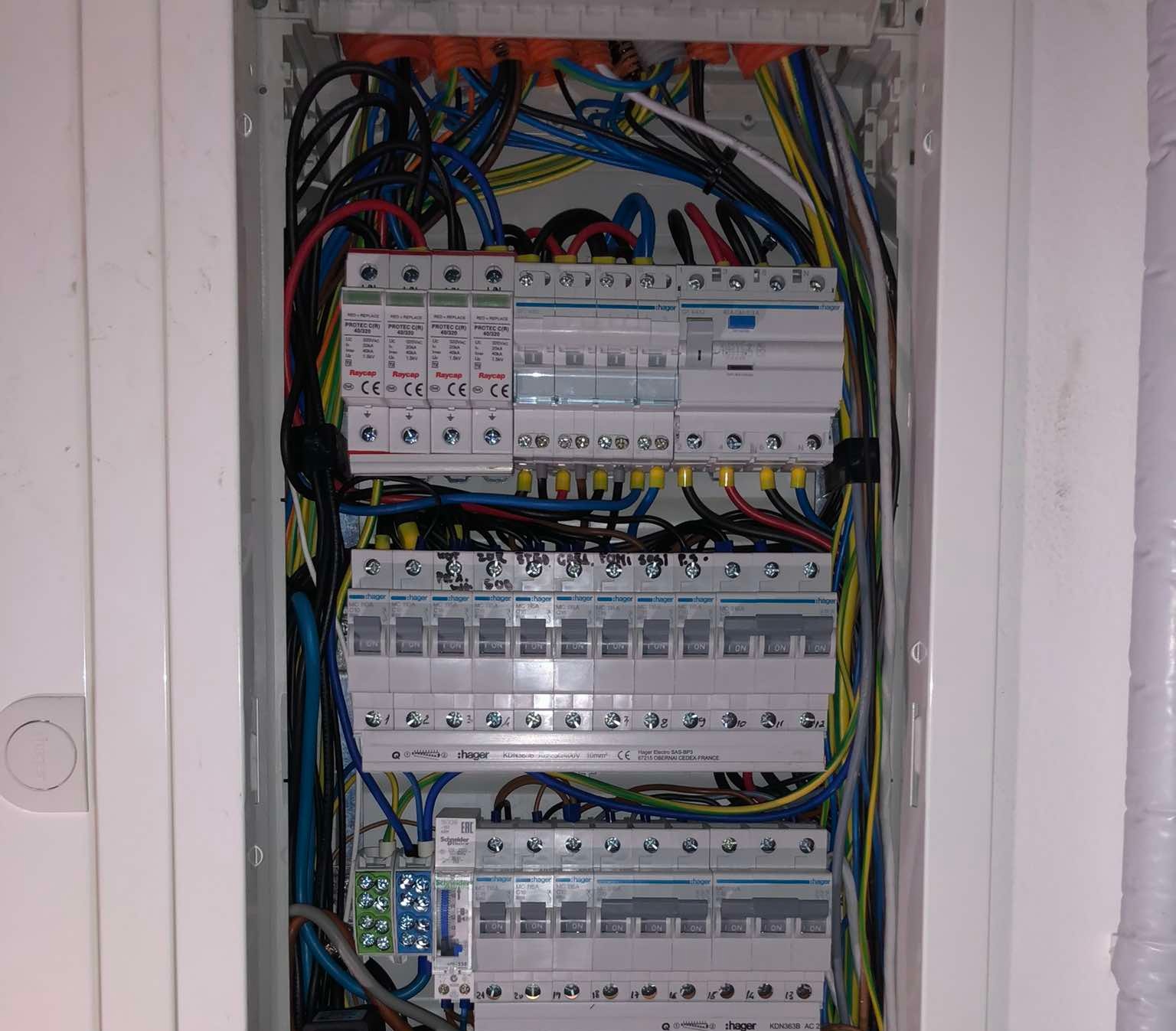
When designing or upgrading an electrical installation, one common question arises: How many circuit breakers can be connected to a single RCD (Residual Current Device)? This article provides a professional overview based on industry standards, practical considerations, and safety regulations.
What Is an RCD and Why Is It Important?
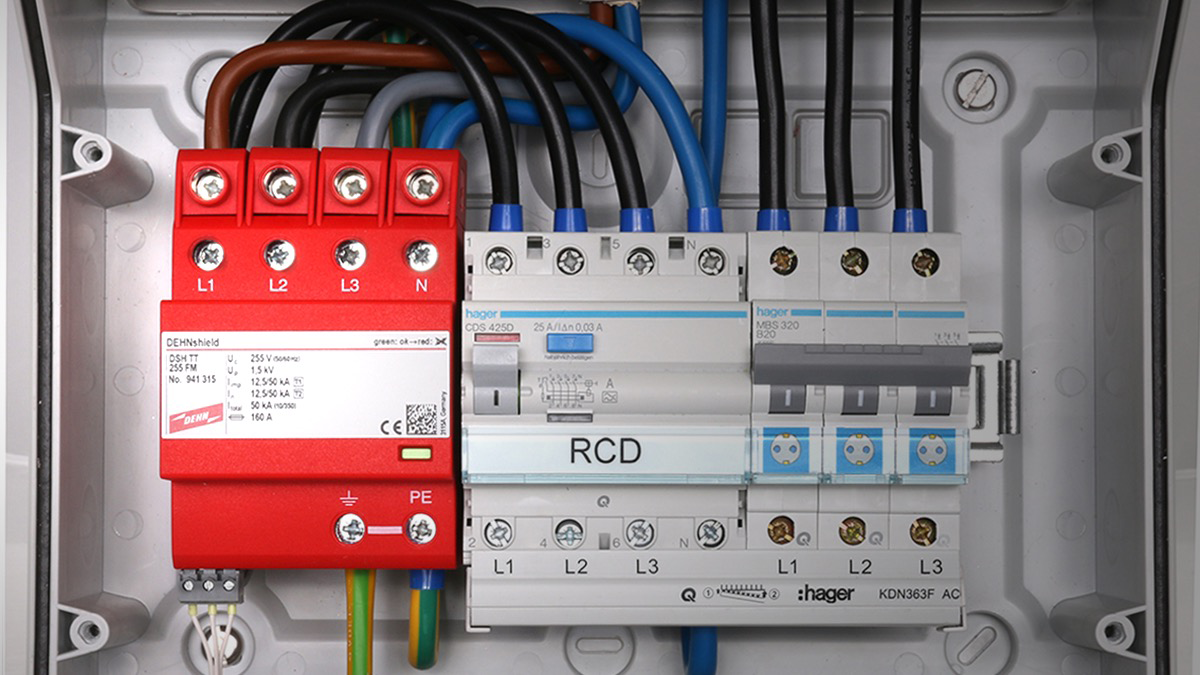
An RCD (Residual Current Device) is a protective device that disconnects the power supply when it detects leakage current to earth, typically 30mA in residential systems. It is designed to protect people from electric shocks and reduce fire risks caused by earth faults.
How Many Circuit Breakers per RCD?
Technically, there is no strict limit to how many MCBs (Miniature Circuit Breakers) can be connected under a single RCD, but there are important practical and safety factors to consider:
1. Total Load Capacity– The total current load of all breakers must not exceed the RCD’s rated current.- Example: A 40A RCD should not be loaded with more than 40A combined from all circuits.
2. Load Balance– Circuits connected to the RCD should be evenly distributed across the phases (for 3-phase systems) and minimize leakage currents.- Imbalance or cumulative leakage may lead to nuisance tripping.
3. Number of Circuits- In residential applications, 4 to 6 circuit breakers per RCD is common practice.- Larger numbers (8 to 10 MCBs) may be used, but increase the chance of whole-group disconnection if a fault occurs.
4. Functional Safety– If one MCB trips due to leakage, the entire RCD disconnects, affecting all connected circuits.- This can be dangerous if critical loads (e.g., fridge, lighting) are connected on the same RCD.
Regulatory Guidelines
European (DIN VDE) Standard
– Recommends selective RCD groups to improve safety and avoid full shutdown.- Some regulations suggest max 6 circuits per RCD in residential buildings.
Germany
– In Germany, it’s common to install separate RCDs for specific areas (e.g., kitchen, bathroom, general sockets) to localize faults and reduce impact.
Best Practices for RCD Distribution
1. Group circuits logically (e.g., lighting, sockets, kitchen).
2. Use Type A or Type F RCDs for modern electronic loads.
3. For high leakage appliances, consider dedicated RCDs.
4. For optimal safety, install individual RCBOs (RCD + MCB in one) per circuit.
Conclusion
While multiple MCBs can be connected to one RCD, the actual number depends on:
– The RCD’s rated current and sensitivity
– Total and leakage load of the connected circuits- Local wiring regulations
– Functionality and safety requirements
For modern installations, minimizing the number of circuits per RCD or using RCBOs is the safest and most flexible approach.





Leave a Reply